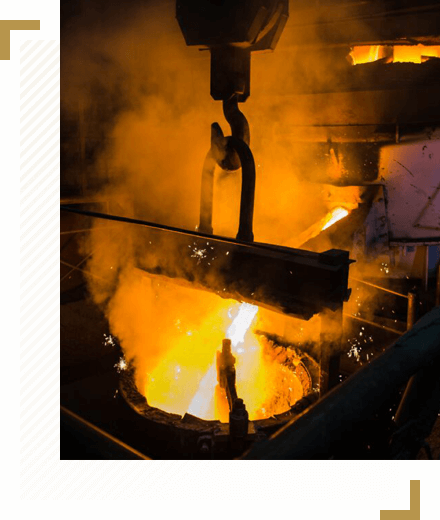
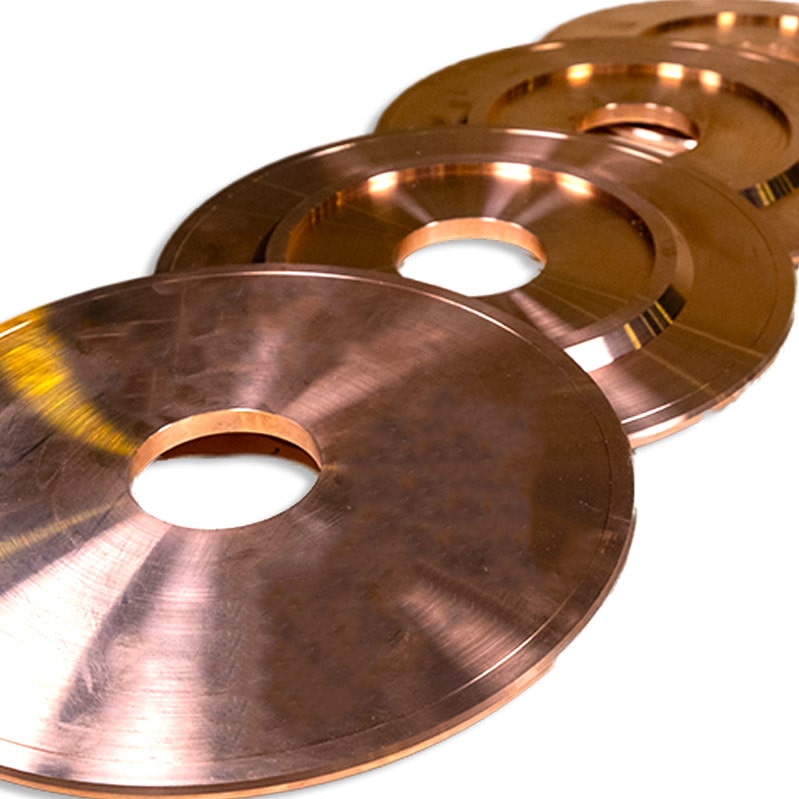
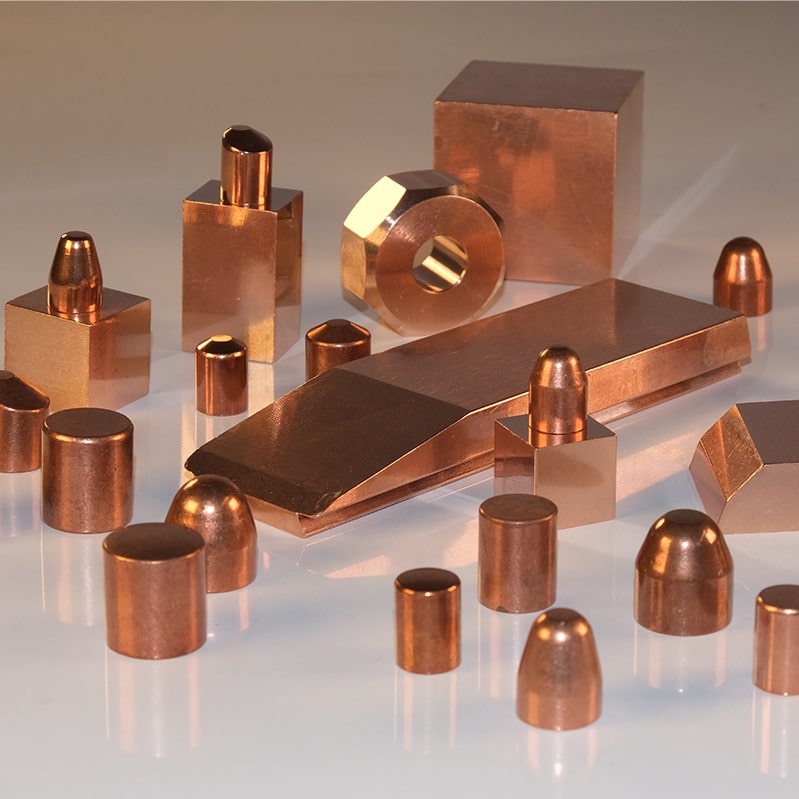
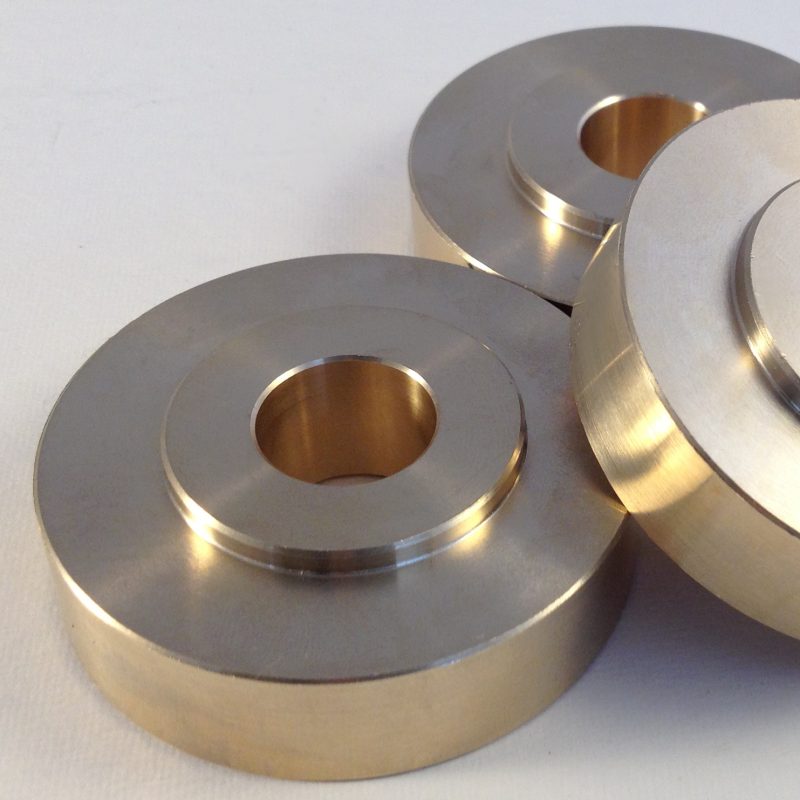
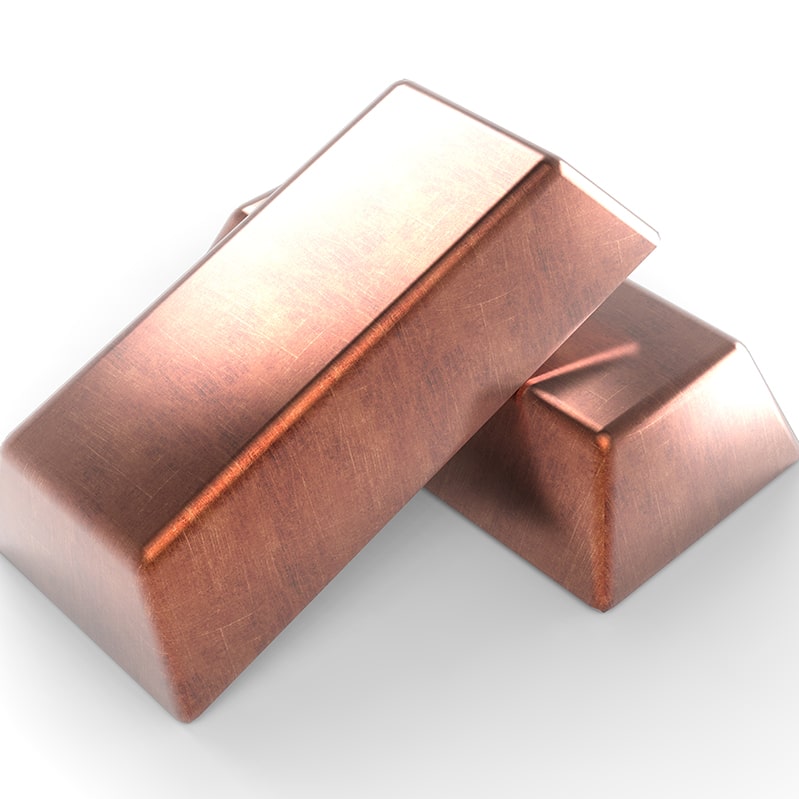
These special alloys can be produced in special sheets, or tubular form, as per the ISO 9100 quality standard. Our capabilities are technical application guidance, casting, heat fabrication and CNC machining.
We provide supply in many areas such as; marine, energy, construction, white goods, mold making, manufacturing, machinery, defense, rail systems, automotive etc. We maintain this vision and growth with our quality certificates.
We have AS 9100, ISO 9001, ISO 27001, ISO 14001, ISO 45001, ISO 10002, ISO 27001 certificates.
Here's why choosing us?
With us you will build a house from scratch, perform the necessary finishing work and fully complete the house. Our experience in construction services is more than 10 years.
-
Sustainability
-
Experience
-
Planning
-
Special Alloys

Here are our special products portfolio
Please ask to our engineers about your special alloys and other types of materials
Why companies choose us?
We have a wide range of customer world wide and they have the similar reasons to choose TCA Inc.
01.
Sustainability
By making clean energy choices we work with conscious resource consumption with the aim to reduce our carbon footprint.

02.
Experience
By using our long years of experience in the sector and our continuous development every day we are able to provide the best quality service to our customers.

03.
Planning
Thanks to our large stock areas and well-planned production systems we are able to offer fast delivery services to our customers.

04.
Special alloys
Our production contains copper alloys which are produced with special processes in accordance with the quality systems as well as customer – specific alloy demands.

Our production expertises...
TCA Inc has its own production lines which is using for a variety of industries such as automotive, home appliance, medical and food, spare part, aviation and space, iron & steel, marine, petro chemistry and mining, railway and so on...

Explore our wide range
usage of applications

Casting
Delivering a liquid metal into a mold that has a negative figure (i.e., a three-dimensional negative image) of the desired shape.

Forging
Involves hammering or pressing the metal to a shape. A hammer or die is used to apply these compressive stresses.

Heat Treatment
A collection of industrial, thermal, and metallurgical techniques that are used to change the physical and chemical properties of a material.

Machining
Controlled material-removal technique that cuts a material to a specified final form and size. We deliver the final product with material certificates and measurement control reports.